
My Blog
-
Tooth Protection and Winter Sports
posted: Jan. 03, 2024.

-
New Year's Eve
posted: Dec. 27, 2023.

-
Teeth Grinding
posted: Dec. 20, 2023.

-
What’s an intraoral camera?
posted: Dec. 13, 2023.

-
‘Tis the Season—for Healthy Dental Choices!
posted: Dec. 06, 2023.

-
Dental X-rays: The Inside Story
posted: Nov. 29, 2023.

-
Thanksgiving Trivia
posted: Nov. 22, 2023.

-
Considerations When Picking the Right Mouthwash
posted: Nov. 15, 2023.

-
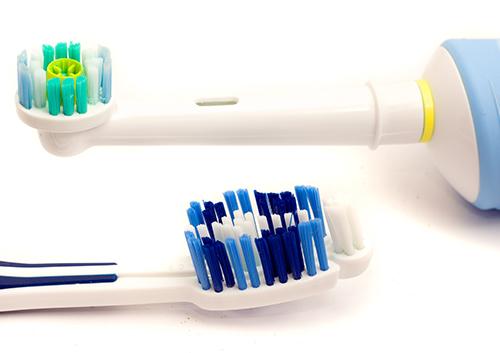
Electric or Manual Toothbrush: Why It Does (and Doesn't) Matter
posted: Nov. 08, 2023.
-
Getting Ready for Winter
posted: Nov. 01, 2023.

-
Halloween: Candy, costumes, and more!
posted: Oct. 25, 2023.

-
Natural Ways to Soothe a Toothache
posted: Oct. 18, 2023.

-
Is soda really bad for your teeth?
posted: Oct. 11, 2023.

-
Fall’s in the Air? Think Fall Dental Care
posted: Oct. 04, 2023.

-
When do children usually lose their baby teeth?
posted: Sep. 27, 2023.

-
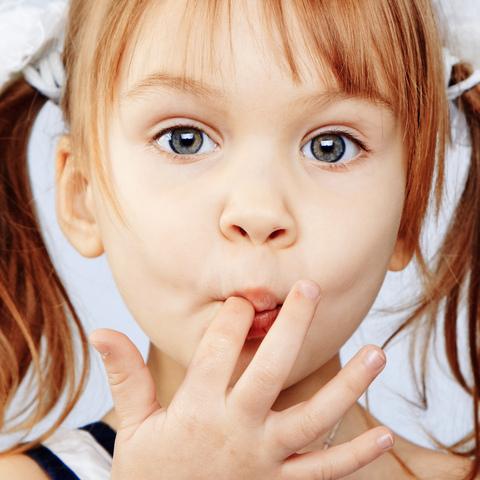
Make Tooth Brushing Fun
posted: Sep. 20, 2023.

This website includes materials that are protected by copyright, or other proprietary rights. Transmission or reproduction of protected items beyond that allowed by fair use, as defined in the copyright laws, requires the written permission of the copyright owners.

